解构赋值
解构赋值的写法
let [a, b, c] = [10, 20, 30];
console.log(a, b, c);
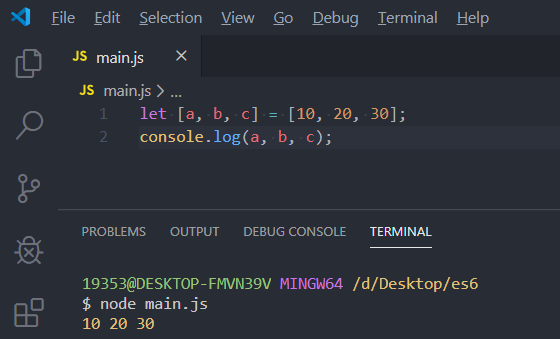
let [x, y, ...other] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(x, y, other);
let {name, age} = {name: 'fmujie', age: 18};
console.log(name, age);
![]()
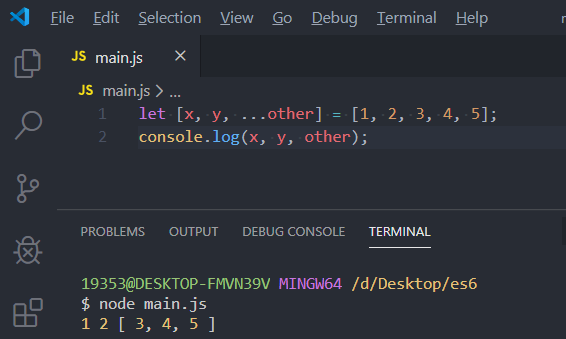
function test() {
return [10, 20];
}
let [num1, num2] = test();
console.log(num1, num2);
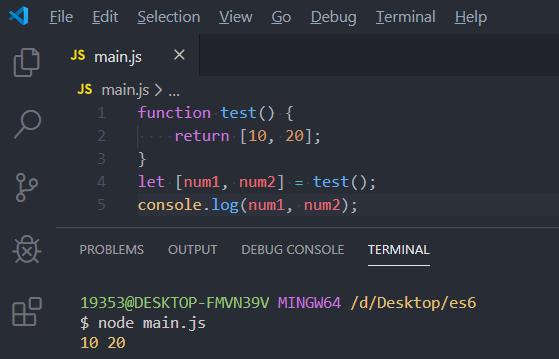
function test({x=3, y=3}) {
return x + y;
}
console.log(test());
console.log(test({x:10}));
console.log(test({y:10}));
console.log(test({x:10, y:20}));
数组循环(for...of)
新的数组循环方式
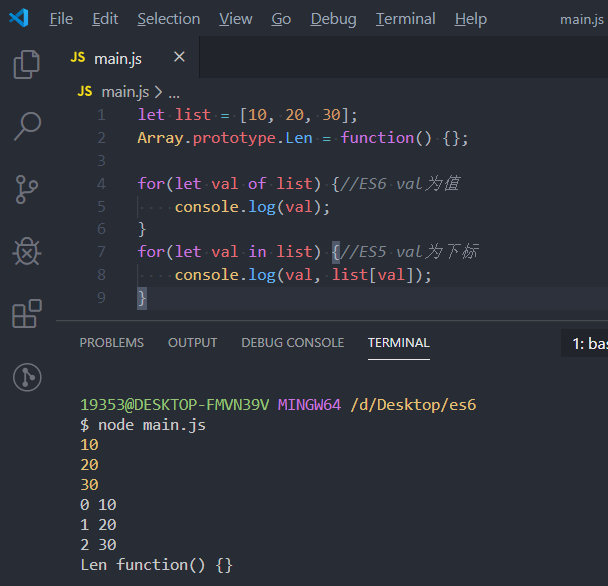
let list = [10, 20, 30];
Array.prototype.Len = function() {};//给数组的属性增加一个方法
for(let val of list) {//ES6 val为值 list当作数组使用 for...of仅仅取出数组的值
console.log(val);
}
for(let val in list) {//ES5 val为下标 list当作变量使用 for...in取出所有属性(循环对象使用)
console.log(val, list[val]);
}
函数的默认值
定义函数时给出参数的默认值
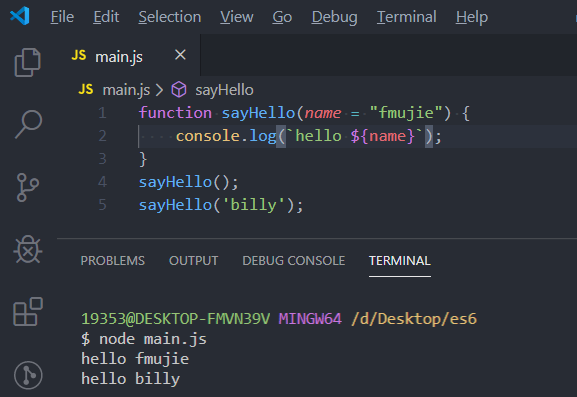
function sayHello(name = "fmujie") {
console.log(`hello ${name}`);
}
sayHello();
sayHello('billy');
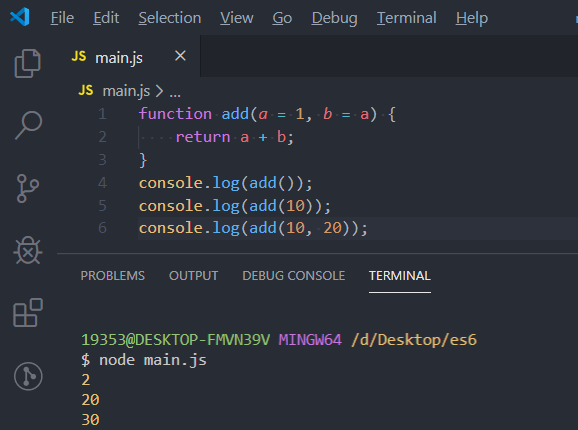
function add(a = 1, b = a) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add());
console.log(add(10));
console.log(add(10, 20));
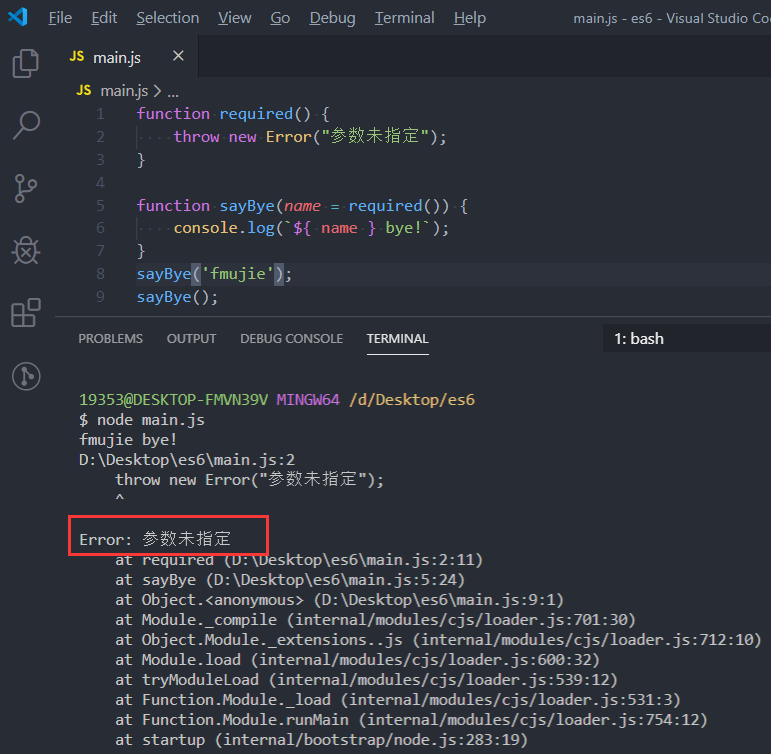
function required() {
throw new Error("参数未指定");
}
function sayBye(name = required()) {
console.log(`${ name } bye!`);
}
sayBye(fmujie);
sayBye();
箭头函数
通过箭头函数简化代码
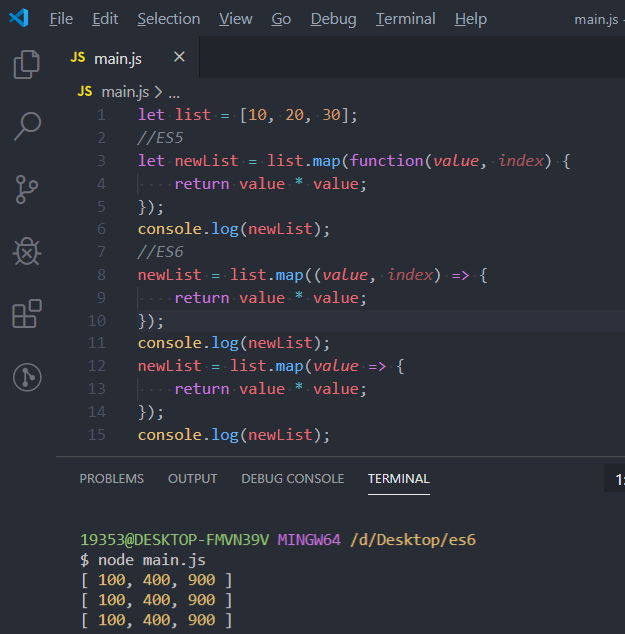
let list = [10, 20, 30];
//ES5
let newList = list.map(function(value, index) {
return value * value;
});
console.log(newList);
//ES6
newList = list.map((value, index) => {
return value * value;
});
console.log(newList);
newList = list.map(value => {
return value * value;
});
console.log(newList);
map()语法
array.map(function(currentValue,index,arr), thisValue)
参数说明
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|
| function(currentValue, index,arr) | 必须。函数,数组中的每个元素都会执行这个函数 函数参数: 参数描述currentValue必须。当前元素的值index可选。当前元素的索引值arr可选。当前元素属于的数组对象 |
| thisValue | 可选。对象作为该执行回调时使用,传递给函数,用作 "this" 的值。 如果省略了 thisValue,或者传入 null、undefined,那么回调函数的 this 为全局对象。 |
可变长参数
定义参数时,可以将参数指定为可变长的数组
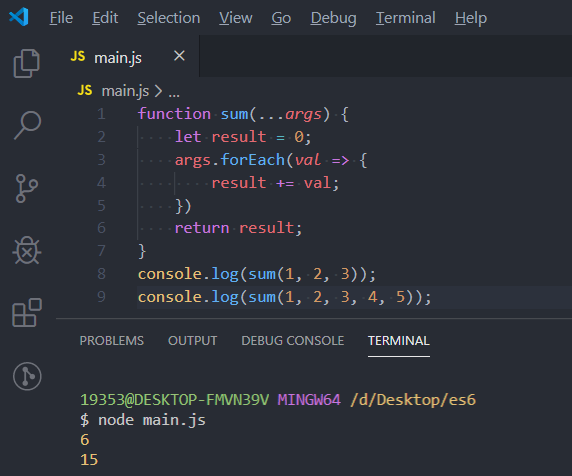
function sum(...args) {
let result = 0;
args.forEach(val => {
result += val;
})
return result;
}
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3));
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
基本对象定义
JS基本对象定义
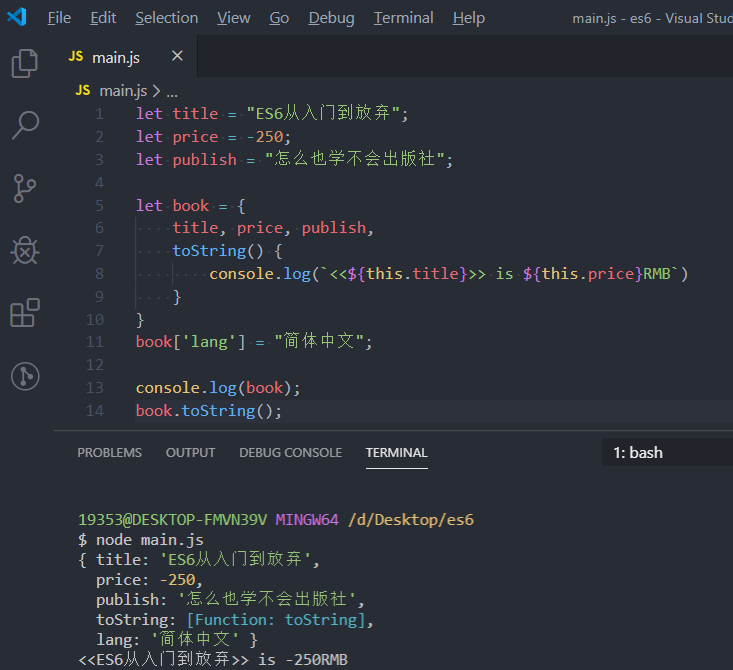
let title = "ES6从入门到放弃";
let price = -250;
let publish = "怎么也学不会出版社";
let book = {
title, price, publish,
toString() {
console.log(`<<${this.title}>> is ${this.price}RMB`)
}
}
book['lang'] = "简体中文";
console.log(book);
book.toString();
类定义
ES6的类定义
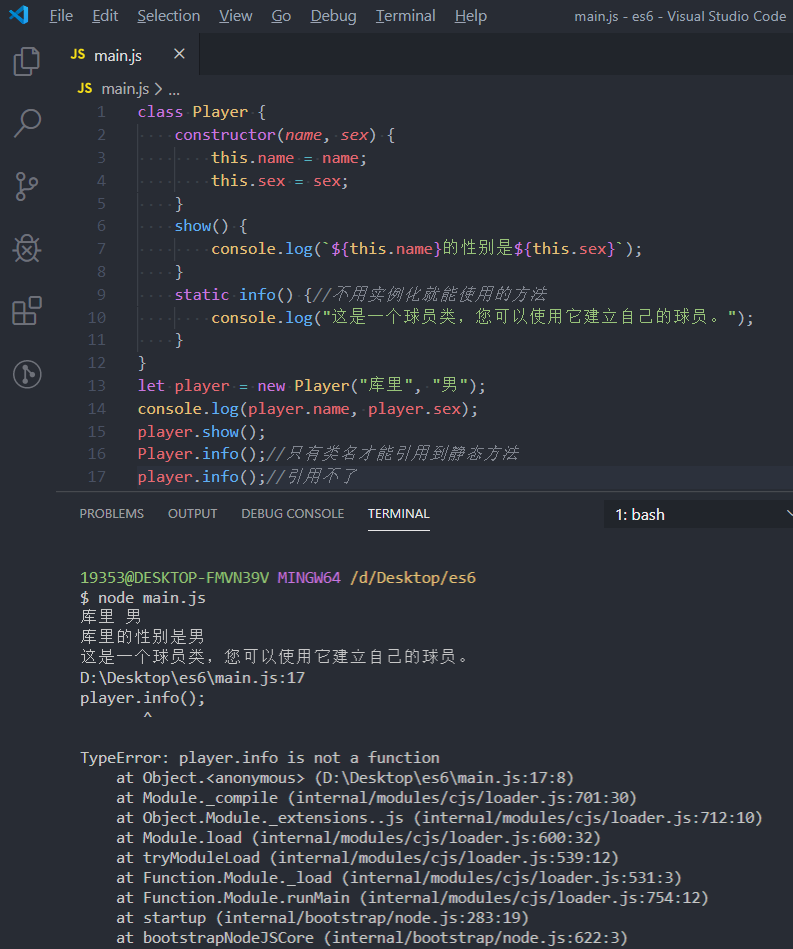
class Player {
constructor(name, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
show() {
console.log(`${this.name}的性别是${this.sex}`);
}
static info() {//不用实例化就能使用的方法
console.log("这是一个球员类,您可以使用它建立自己的球员。");
}
}
let player = new Player("库里", "男");
console.log(player.name, player.sex);
player.show();
Player.info();//只有类名才能引用到静态方法
player.info();//引用不了
setter/getter的定义
在类中定义setter/getter方法
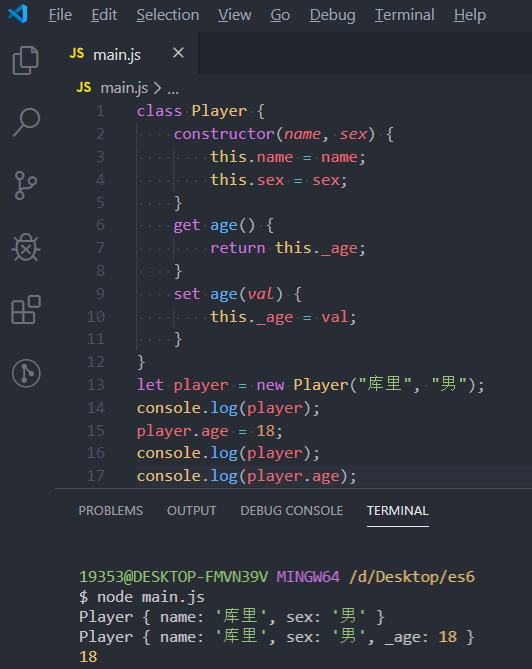
class Player {
constructor(name, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
get age() {
return this.age;
}
set age(val) {
this.age = val;
}
}
let player = new Player("库里", "男");
player.age = 18;
console.log(player);
类继承
ES6面向对象的编程之类继承
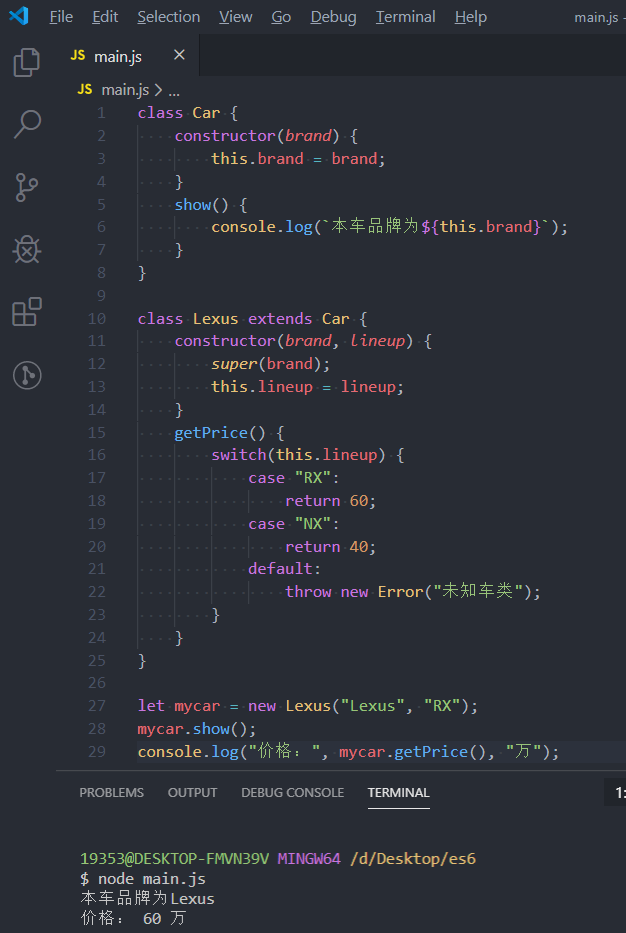
class Car {
constructor(brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
show() {
console.log(`本车品牌为${this.brand}`);
}
}
class Lexus extends Car {
constructor(brand, lineup) {
super(brand);
this.lineup = lineup;
}
getPrice() {
switch(this.lineup) {
case "RX":
return 60;
case "NX":
return 40;
default:
throw new Error("未知车类");
}
}
}
let mycar = new Lexus("Lexus", "RX");
mycar.show();
console.log("价格:", mycar.getPrice(), "万");
ES6入门系列说明:本系列仅仅作为ES6入门教学视频的归纳总结与记录,在此感谢小马视频ORYouTube地址















还不快抢沙发